Student Management System Database
A comprehensive PostgreSQL database schema for managing academic institutions, supporting student lifecycle management, course enrollment, and complex academic workflows.
🏗️ Database Architecture Overview
The database follows a normalized relational design with clear separation between:
- Core academic entities (students, courses, classes)
- Supporting reference data (faculties, programs, statuses)
- Audit and validation tables (history, rules, patterns)
The schema supports complex academic workflows including student lifecycle management, course prerequisites, class enrollment, and status transition rules.
📊 Entity Relationship Diagram
The system is built around these core relationships:
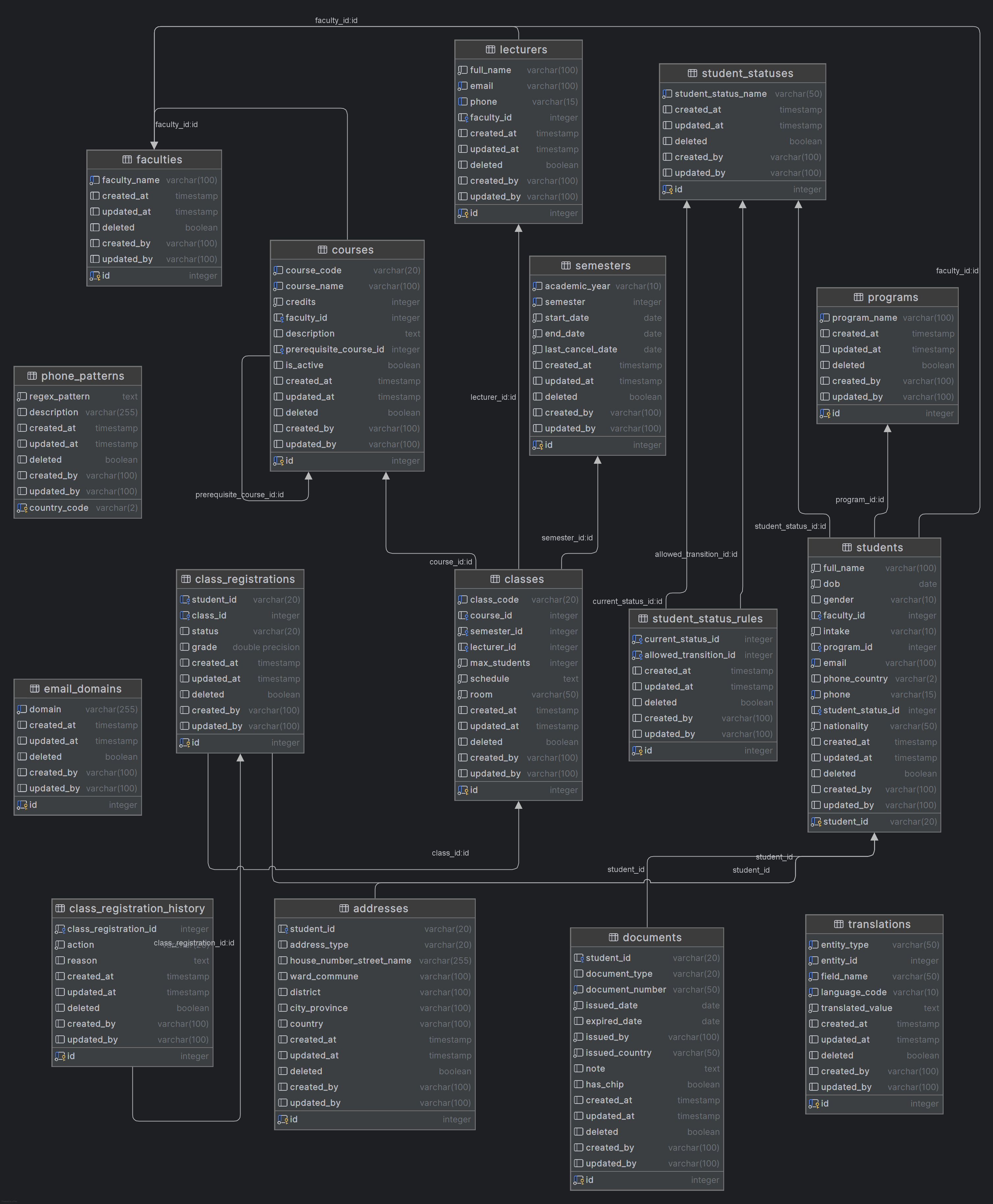
🗂️ Database Schema
Core Entity Tables
Student Management
| Table | Primary Key | Purpose | Key Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|
students | student_id (VARCHAR) | Core student information | Unique email, phone; gender check constraint |
addresses | id (SERIAL) | Student address records | Multiple address types per student |
documents | id (SERIAL) | Identity documents | Unique document numbers; date validations |
Key Features:
- Custom VARCHAR student IDs supporting institutional formats
- Gender field with Vietnamese language values (
'Nam', 'Nữ', 'Khác') - International phone number support with country codes
- Multiple address types per student
Academic Reference Tables
| Table | Purpose | Key Fields | Business Rules |
|---|---|---|---|
faculties | Academic departments | faculty_name (unique) | Soft deletion support |
programs | Study programs | program_name (unique) | References academic tracks |
student_statuses | Enrollment status | student_status_name (unique) | Supports status transitions |
Sample Data:
- Faculties: "Khoa Luật", "Khoa Tiếng Anh thương mại"
- Student Statuses: "Đang học", "Đã tốt nghiệp", "Đã thôi học", "Tạm dừng học"
Course and Class Management
Academic Catalog Structure
- Courses: Support hierarchical relationships with prerequisites
- Classes: Specific course offerings with enrollment limits
- Semesters: Academic periods with date validation
- Lecturers: Faculty members assigned to classes
Key Features:
- Self-referencing course prerequisites
- Active/inactive course status management
- Complex semester date validation
- Instructor assignment tracking
Registration and Enrollment
Class Registration Status Flow
| Status | Description | Grade Allowed |
|---|---|---|
REGISTERED | Active enrollment | No |
CANCELLED | Withdrawn before completion | No |
COMPLETED | Finished with grade | Yes (0-10 scale) |
Audit Trail
class_registration_historymaintains complete audit trail- All status changes tracked with timestamps and reasons
- Supports compliance requirements and dispute resolution
🔄 Student Status State Machine
The system enforces valid student status transitions:
New Enrollment → DangHoc (Active Student)
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────┐
↓ ↓
TamDungHoc (On Leave) ←→ DaThoiHoc (Withdrawn)
↓ ↓
DangHoc ←─────────────────────────────┤
↓ ↓
DaTotNghiep (Graduated) ←─────────────┘
Status transitions are enforced through the student_status_rules table with foreign key constraints.
✅ Business Rules and Validation
Validation Support Tables
| Table | Purpose | Key Fields |
|---|---|---|
phone_patterns | Country-specific phone validation | country_code (PK), regex_pattern |
email_domains | Allowed email domains | domain (unique) |
Phone Validation: Supports international formats including Vietnam (+84), USA (+1), UK (+44), and 16 other countries.
Email Validation: Restricts registration to approved institutional or testing domains.
Constraint Patterns
All tables follow consistent patterns:
| Pattern | Implementation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Soft Deletion | deleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE | Preserve data for audit |
| Audit Trail | created_at, updated_at, created_by, updated_by | Track changes |
| Unique Constraints | Business key uniqueness | Prevent duplicates |
| Check Constraints | Domain value validation | Enforce business rules |
🚀 Database Setup
Prerequisites
- PostgreSQL 12+
- Database user with CREATE privileges
Installation Steps
-
Create Database
CREATE DATABASE student_management; -
Run Schema Creation
psql -d student_management -f server/src/main/resources/db/1_create_table.sql -
Insert Sample Data
psql -d student_management -f server/src/main/resources/db/2_insert_data.sql
Table Creation Order
Due to foreign key dependencies, tables must be created in this order:
- Reference Tables:
faculties,student_statuses,programs - Core Tables:
students,courses,semesters,lecturers - Relationship Tables:
addresses,documents,classes,class_registrations - Business Rule Tables:
student_status_rules,phone_patterns,email_domains - Audit Tables:
class_registration_history
📝 Sample Data
The initialization includes comprehensive sample data:
- 20 students with diverse international backgrounds
- 4 faculties representing different academic departments
- 10 courses with prerequisite relationships
- 10 classes across multiple semesters
- Complete address and document records for select students
- Phone validation patterns for 19 countries
- Status transition rules for all valid state changes
📁 File Structure
server/src/main/resources/db/
├── 1_create_table.sql # Schema definition
└── 2_insert_data.sql # Sample data insertion
🤝 Contributing
When modifying the schema:
- Update both SQL files
- Test with sample data
- Update this README
- Consider migration scripts for existing data
📄 License
This database schema is part of the Student Management System project.